Introduction: The Fintech Revolution in Bangladesh
The global rise of financial technology (fintech) has dramatically transformed how people save, spend, borrow, and invest. In Bangladesh, the fintech revolution is progressing at an extraordinary pace. With over 160 million people, increasing mobile penetration, and growing digital literacy, the country is becoming a fertile ground for fintech innovation.
In this article, we’ll explore the current fintech Industry in Bangladesh, highlighting its evolution, major players, key growth drivers, persistent challenges, and untapped opportunities shaping the industry’s future.

What is Fintech and How It’s Transforming Bangladesh’s Financial Landscape
Fintech refers to the integration of technology with financial services to make transactions faster, more secure, and more accessible. In Bangladesh, fintech has become a catalyst for financial inclusion, particularly in rural and underserved areas.
For years, limited access to traditional banking services hindered financial inclusion. Now, mobile wallets and digital payment platforms—like Bkash, Rocket, and Nagad—are enabling millions to access essential financial services via smartphones. Fintech is no longer just a trend; it’s becoming a way of life for many Bangladeshis.
A Brief History of Fintech
FinTech 1.0 (1866 – Early 1960s)
- The foundation of fintech began with technological innovations like the telegraph and later, the first ATM.
- The focus was on improving traditional banking infrastructure with early automation tools.
FinTech 2.0 (1967 – 2000s)
- Introduction of electronic stock exchanges, credit cards, and online banking.
- Banks began adopting digital infrastructure to offer more convenience to customers.
FinTech 3.0 (2008 – Present)
- A boom in cryptocurrencies, mobile wallets, and peer-to-peer lending.
- Apps like PayPal and Stripe transformed global financial transactions.
FinTech 4.0 (The Near Future)
- Emerging technologies like AI, blockchain, and smart contracts are leading the next wave.
- Innovations in insurtech, regtech, and wealthtech are redefining service delivery.

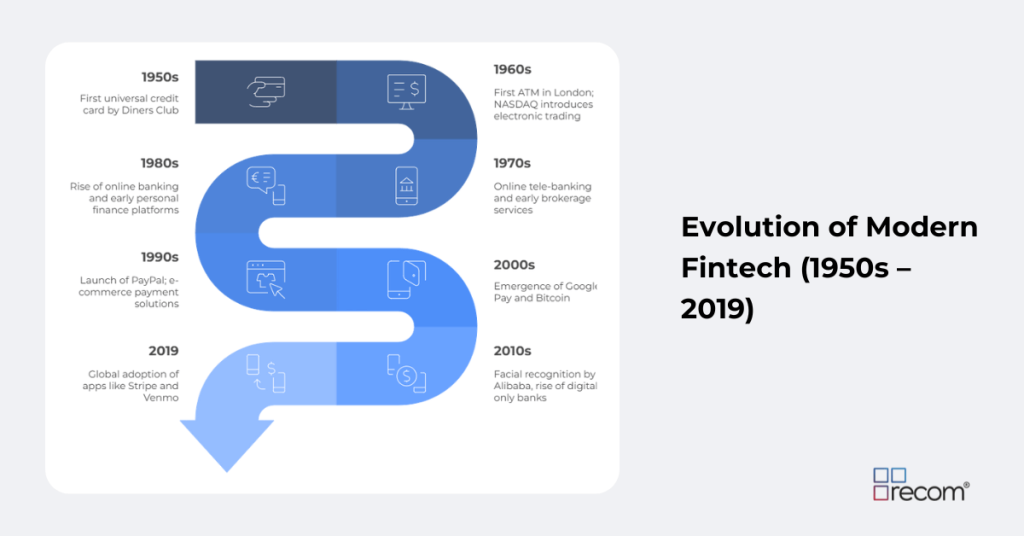
Evolution of Modern Fintech (1950s–2019)
| Decade | Key Developments |
| 1950s | First universal credit card by Diners Club |
| 1960s | First ATM in London; NASDAQ introduces electronic trading |
| 1970s | Online tele-banking and early brokerage services |
| 1980s | Rise of online banking and early personal finance platforms |
| 1990s | Launch of PayPal; e-commerce payment solutions |
| 2000s | Emergence of Google Pay and Bitcoin |
| 2010s | Facial recognition by Alibaba, rise of digital-only banks |
| 2019 | Global adoption of apps like Stripe and Venmo |
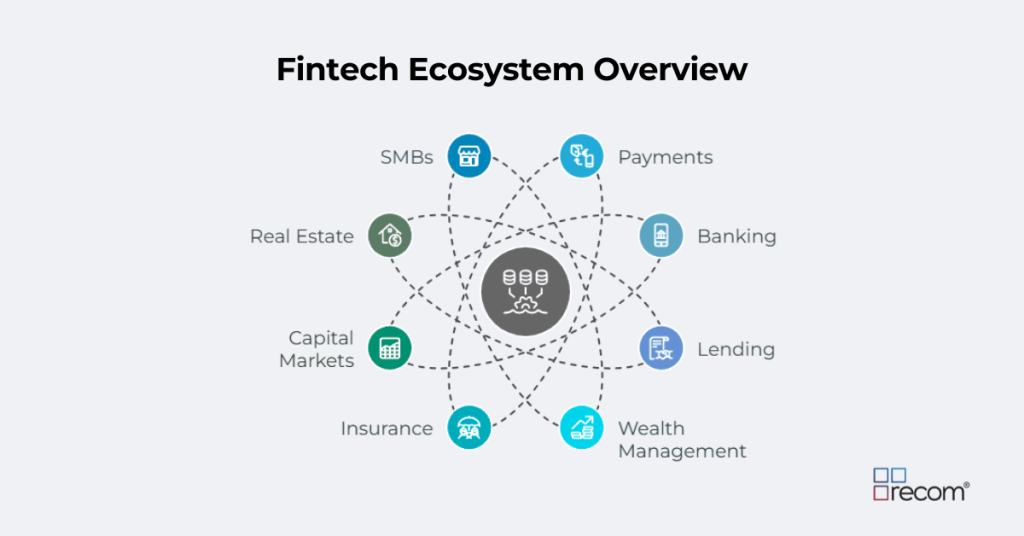
Fintech Ecosystem Overview: What Does Fintech Cover?
Fintech in Bangladesh spans across several domains:
- Payments – Mobile payments, remittances, and POS solutions
- Banking – Digital banks (neobanks), account management
- Lending – Peer-to-peer lending, microloans, SME financing
- Wealth Management – Investment platforms, robo-advisors
- Insurance – Online insurance, claim automation, insurtech
- Capital Markets – Trading platforms, data analytics
- Real Estate – Online mortgage and property finance tools
- SMBs – Invoicing, accounting, and payment gateways
Key Drivers of Fintech Growth in Bangladesh
1. Government Support and Regulations
The Bangladeshi government has been proactive in enabling fintech growth through initiatives like the National Payment Switch Bangladesh (NPSB) and mobile financial services (MFS) regulations. Bangladesh Bank plays a pivotal role in encouraging innovation while maintaining financial stability.
2. Rising Mobile and Internet Penetration
Bangladesh boasts 170+ million mobile subscribers. Rapid smartphone adoption and growing mobile internet access have made digital financial services more accessible—even in remote regions.
3. Financial Inclusion
Fintech is closing the gap between the unbanked and formal financial services. Platforms like Bkash and Nagad have empowered tens of millions of Bangladeshis to manage money digitally—boosting economic participation across all demographics.

Top Fintech Companies in Bangladesh
1. Bkash – The Pioneer
Founded in 2011, Bkash is the leading mobile financial service in the country. It supports money transfers, utility bill payments, airtime purchases, and more. Backed by BRAC Bank and strategic investors like the IFC and Ant Group, Bkash leads with a robust agent network and innovative services.
2. Rocket – Backed by Dutch-Bangla Bank
Rocket is one of the earliest mobile money services and integrates directly with Dutch-Bangla Bank’s infrastructure. It offers users a secure, reliable experience with wide coverage.
3. Nagad – The Disruptor
Launched by the Bangladesh Post Office, Nagad has quickly gained popularity due to its low transaction fees and ease of use. With innovative account onboarding (no internet required), Nagad is democratizing financial access like never before.
Challenges Facing the Fintech Industry in Bangladesh
1. Digital Literacy Gaps
Many users, especially in rural areas, lack the skills to navigate fintech apps. While programs promoting digital education exist, more grassroots efforts are needed to scale adoption.
2. Cybersecurity Risks
As digital finance grows, so do threats like fraud, phishing, and data breaches. Fintech companies must invest in cybersecurity infrastructure, user authentication, and real-time fraud detection.
3. Infrastructure Limitations
Although mobile use is widespread, many rural areas still suffer from unstable connectivity, affecting service reliability. Continuous investment in telecom and tech infrastructure is essential.
Opportunities for Fintech Industry in Bangladesh
1. Reaching the Rural Economy
Nearly two-thirds of Bangladesh’s population lives in rural areas. Customized fintech solutions for agriculture, small businesses, and rural remittances represent a massive untapped market.
2. Cross-Border Remittance
Bangladesh is one of the largest remittance receivers globally. Fintech platforms offering low-cost, instant, and transparent cross-border transfers could capture significant market share.
3. Government–Private Sector Synergy
Collaborative efforts between regulators and fintech companies can drive digital financial transformation. Sandboxes, innovation hubs, and public funding for fintech startups can further accelerate growth.
Conclusion: The Road Ahead for Fintech Industry in Bangladesh
Bangladesh’s fintech sector stands at a pivotal moment. With strong policy backing, a growing digital population, and pressing demand for inclusive financial services, the country is on track to become a regional fintech leader.
For entrepreneurs, investors, and innovators, Bangladesh offers a dynamic environment full of real-world problems to solve and scalable business models to develop. The next chapter of this revolution will be written by those who dare to innovate.
Interested in exploring fintech investment or launching your solution in Bangladesh? Let’s connect and discuss how to turn these insights into action. Reach out to our team today!
FAQs
What is fintech in Bangladesh?
Fintech in Bangladesh refers to digital platforms delivering financial services like mobile wallets, digital payments, and online banking to both banked and unbanked populations.
Which are the leading fintech companies in Bangladesh?
Top players include Bkash, Rocket, and Nagad, serving millions through mobile financial services.
What challenges does the fintech industry face?
Key issues include low digital literacy, cybersecurity vulnerabilities, and poor infrastructure in rural areas.
How is the government supporting fintech growth?
Through regulatory initiatives, payment infrastructure, and public-private partnerships like NPSB and MFS guidelines.
What opportunities exist in the fintech sector?
Opportunities include expanding services in rural areas, streamlining remittances, and scaling through government collaboration.